Science

Summary
Key Stage 3 Science at Gordon’s enables students to engage in understanding and learning Science as well as applying their knowledge to a myriad of contexts. Students study Biology, Chemistry and Physics separately and develop their understanding of Working Scientifically through the use of practical work. Our aim is to maintain curiosity, while preparing them for future learning.
There are many extra-curricular opportunities including trips and competitions. Year 7 and 8 undertake a specific period of Enrichment in the Summer term, centring around topics taught that year in each of the three Sciences. Years 7 to 9 also have the opportunity to take part in Gordon’s Sudan Prize.
Head of Department: Mrs Beecham abeecham@gordons.school

Summary
The department has a very strong academic record at both GCSE. Students take either the three Separate Sciences (Biology, Chemistry and Physics) gaining three GCSEs, or Combined Science (Trilogy) equivalent to two GCSEs. We follow the AQA syllabus for all our GCSE qualifications.
Alongside specification content, there is a strong emphasis placed on Working Scientifically, a key component of the GCSE specifications. Students undertake Required Practicals in each of the three Sciences and these are then examined in their GCSE exams. These practical activities help to develop our students’ analytical skills benefitting their subject understanding.
Course details
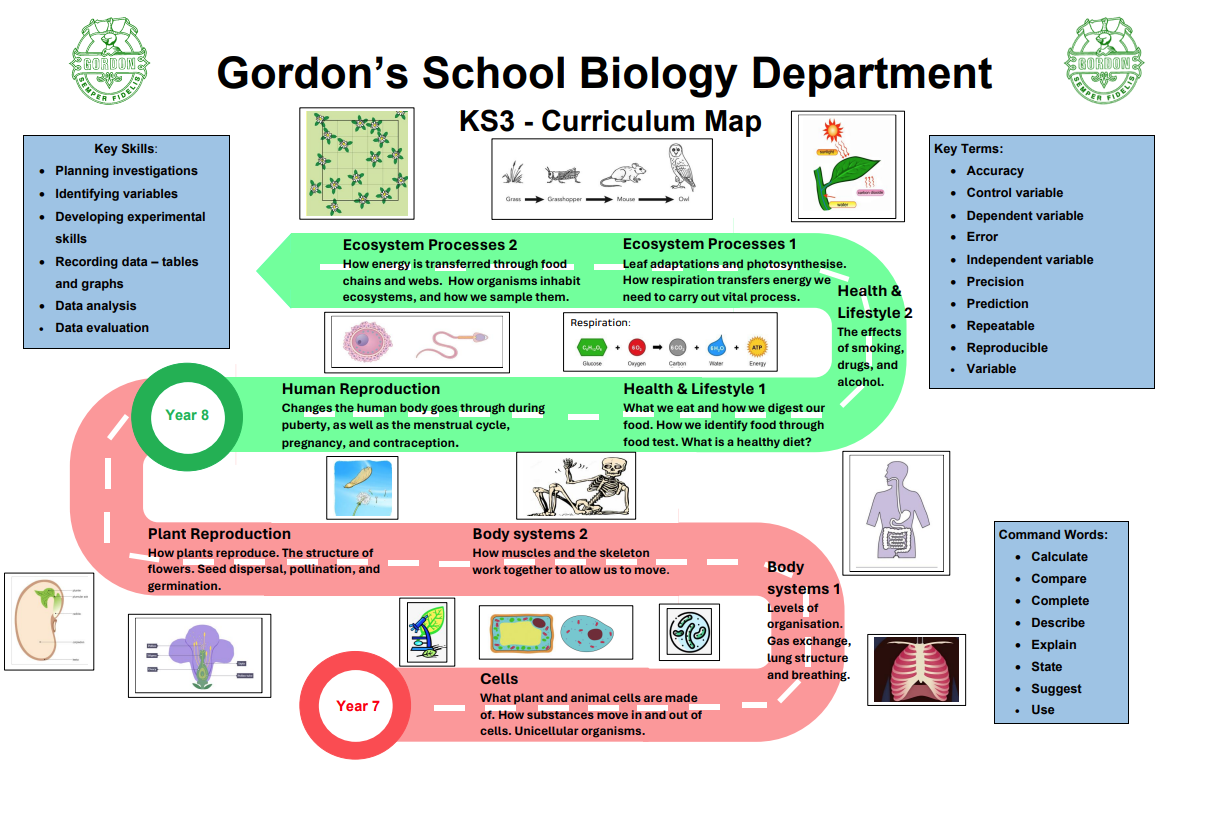
Biology
- Cell biology
- Organisation
- Infection and response
- Bioenergetics
- Homeostasis and response
- Inheritance, variation and evolution
- Ecology
TYPICAL ACTIVITIES
Practical experiments, group and pair work, individual research topics, class discussions and demonstrations.
Chemistry
- Atomic structure and the periodic table
- Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter
- Quantitative chemistry
- Chemical changes
- Energy changes
- The rate and extent of chemical change
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical analysis
- Chemistry of the atmosphere
- Using resources
TYPICAL ACTIVITIES
Practical experiments, group and pair work, individual research topics, class discussions and demonstrations.
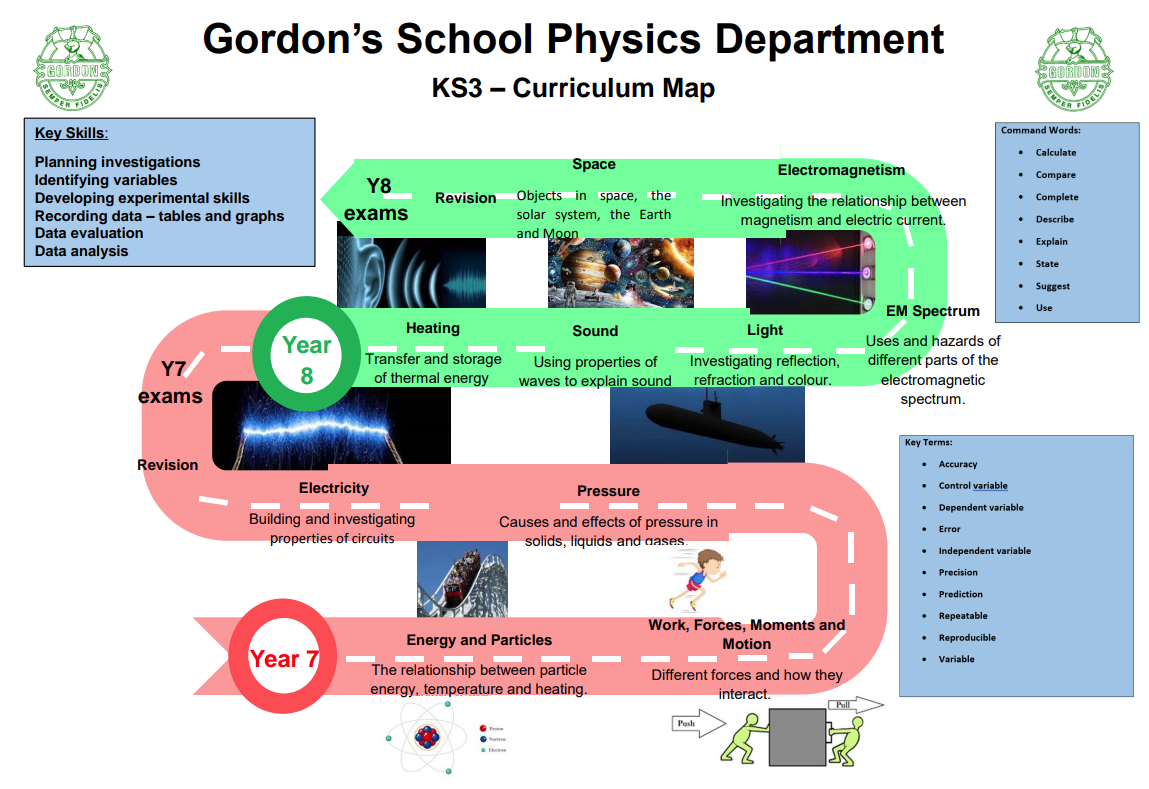
Physics
- Energy
- Electricity
- Particle model of matter
- Atomic structure
- Forces
- Waves
- Magnetism and electromagnetism
- Space physics
TYPICAL ACTIVITIES
Practical experiments, group and pair work, individual research topics, class discussions and demonstrations.
Combined Science
- Cell biology
- Organisation
- Bioenergetics
- Infection and response
- Homeostasis and response
- Inheritance, variation and evolution
- Ecology
- Atomic structure and the periodic table
- Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter
- Quantitative chemistry
- Chemical changes
- Energy changes
- The rate and extent of chemical
- change
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical analysis
- Chemistry of the atmosphere
- Using resources
- Energy
- Electricity
- Particle model of matter
- Atomic structure
- Forces Waves
- Magnetism and electromagnetism
TYPICAL ACTIVITIES
Practical experiments, group and pair work, individual research topics, class discussions and demonstrations.

Summary
All three Sciences are popular choices for further study at A Level, with many of our students electing to study Science or Science-related courses at some of the top universities in the country. We follow the AQA syllabus for all our A Level qualifications. Students are offered opportunities to attend lectures and to participate in National competitions including Olympiads.
Biology is the study of living systems. The subject covers a wide array of knowledge encompassing aspects of life from molecular levels, through cells, tissues and organisms and on to populations and ecosystems. This wide spectrum is reflected in the structure of the A Level course and enables students to go on to higher study at university or enter a science-based workplace.
A Level Chemistry is the science of the composition, structure, properties and reactions of matter, understood in terms of atoms, atomic particles and the way they are arranged and link together. It is concerned with the synthesis, formulation, analysis and characteristic properties of substances and materials of all kinds. Sometimes referred to as the 'central science', Chemistry helps to connect physical sciences, like Maths and Physics, with applied sciences, such as Biology, Medicine and Engineering. Chemistry is one of the Russell Group universities' 'facilitating' subjects — so called because choosing them at A-level allows a wide range of options for degree study.
Physics is the study of why everything is the way it is and how the Universe works. A Level Physics begins to explore the fundamental workings of the world around us, from the particles that make up all matter to the forces involved in the Big Bang, taking in the bizarre possibilities of Quantum physics along the way.
Course details
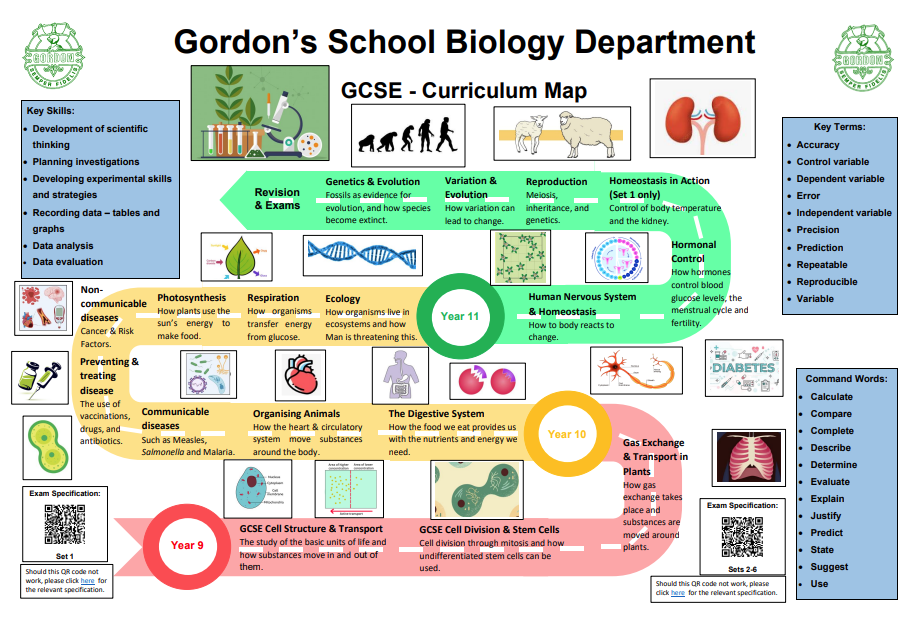
Biology
Topic 1: Biological Molecules
Topic 2: Cells
Topic 3: Organisms exchange substances with their environment
Topic 4: Genetic information, variation and relationships between organisms
Topics 1 – Four taught in Year 12. Also in Year 12 students complete six Required Practicals. These will be assessed in the exams.
Topic 5: Energy transfers in and between organisms
Topic 6: Organisms respond to changes in their internal and external environment
Topic 7: Genetics, populations, evolution and ecosystems
Topic 8: The control of gene expression
Topics 5 – Eight taught in Year 13. Also in Year 13 students complete six Required Practicals. These will be assessed in the exam.
Chemistry
Year 12
Physical chemistry: Atomic structure, Amount of substance, Bonding, Energetics, Kinetics, Chemical equilibria, Le Chatelier’s principle and Kc, oxidation, reduction and redox equations.
Inorganic chemistry: Groups 2 the alkaline earth metals, Group 7 the halogens, periodicity.
Organic chemistry: Introduction to organic chemistry, Alkanes, Halogenoalkanes, Alkenes, Alcohols, Organic analysis.
Also in Year 12 students complete six Required Practicals. These will be assessed in the exams.
Year 13
All of the above in addition to the following topics:
Physical chemistry: Thermodynamis, Acids and Bases, Electrode potentials and electrochemical cells, Rate equations, Equilibrium constant Kp for homogeneous systems.
Inorganic chemistry: Transition metals, Reactions of ions in aqueous solution, Properties of Period 3 elements and their oxides.
Organic chemistry: Optical isomerism, Aldehydes and ketones, Carboxylic acids and derivatives, Aromatic chemistry, Amines, Polymers, Amino acids, proteins and DNA, Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, Chromatography, Organic synthesis. Also in Year 13 students complete 6 Required Practicals. These will be assessed in the exams and provide the evidence for the Practical Endorsement.
Physics
Topic 1: Particles and radiation
Topic 2: Waves
Topic 3: Mechanics and materials
Topic 4: Electricity
Topics 1 – Five taught in Year 12. Also in Year 12 students complete 6 required practicals. These will be assessed in public examinations.
Topic 5: Further Mechanics and Thermal Physics
Topic 6: Fields and their consequences
Topic 7: Nuclear Physics
Topic 8: Optional Topic
Topics 6 – 9 taught in Year 13. Also in Year 13 students complete six more required practicals. These will be assessed in public examinations.
Entry Criteria
Biology: GCSE grade 7 in Biology or 7-7 in Combined Science.
Chemistry: GCSE grade 7 in Chemistry or 7-7 in Combined Science.
Physics: GCSE grade 7 in Physics or 7-7 in Combined Science and must take A Level Mathematics in Year 12.